Plaidbot
Plaidbot is a set of tools that allows you to predict the author of a Slack message using a BERT-based classifier that is trained on your channel’s previous Slack history.
Example:

The process involves the following steps:
- Exporting your slack message history from your Slack settings
- Training a BERT-based model using this message history to predict the user based on the message text
- Uploading the trained model to a hosted repository (HuggingFace)
- Deploying a Flask Web Application that fetches and loads the trained model from this repository
- Exposing an endpoint on the web app that accepts a piece of text, which is fed into the loaded model
- This loaded model predicts the user, which is sent back as a response to the web request
- The web app can be called via a Slack command, e.g. /predict “This is a test message!”
These steps are illustrated in the following diagram:
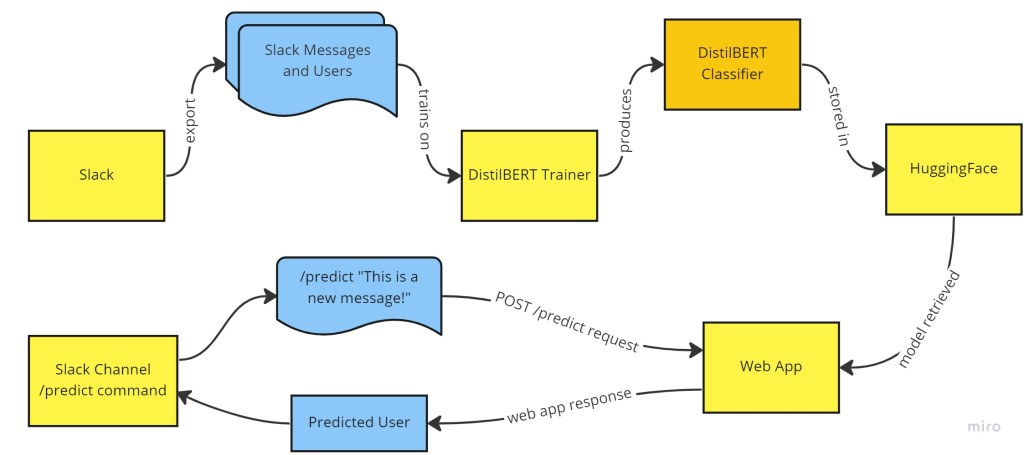
The details and tools needed to perform all of these steps are contained in the README file of the project’s Github repository. It can be up and running in a manner of 30 minutes.
This project uses DistilBERT, which is a BERT-based classifier. These transformer-based model are very resource intensive and can take a long time to train. It is recommended that you perform the training using Google CoLab and that you upgrade to a premium tier so that you can use a GPU while training. This makes the training significantly faster.
NLP Quote Finder
This is a project that makes use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to identify quotes that a given user may like. It is a similar process for how emails might be labeled as ham or spam.
The engine must start with a series of quotes that a user has labelled as either liking or disliking. The user can request a random quote and then make a POST request to the server indicating whether or not they liked or disliked it.

The engine then analyzes certain features of those pre-labelled quotes, such as length of words, words/sentence, total number of words, as well as the words themselves. A model is built based on these features and stored on the server. The user can then request another random quote, and the engine will predict whether or not the user will like it, by indicating true/false in the response body.

This project is largely a proof of concept for deploying a working NLP pipeline into a production environment. Future work includes expanding the training data to have more examples from which to build the engine, and also making a front-end web application.
Machine Learning Algorithms From Scratch
This is a repository that contains notebooks for building traditional machine learning algorithms from scratch in Python. The notebooks include relevant theory, useful examples, and performance comparison with the sklearn algorithms. Some of the algorithms are quite complex, especially SVM, so some of the deeper theory and functionality is skipped.
Algorithms
- K-nearest neighbours
- Decision Trees
- Naive Bayes
- Logistic Regression
- SVM